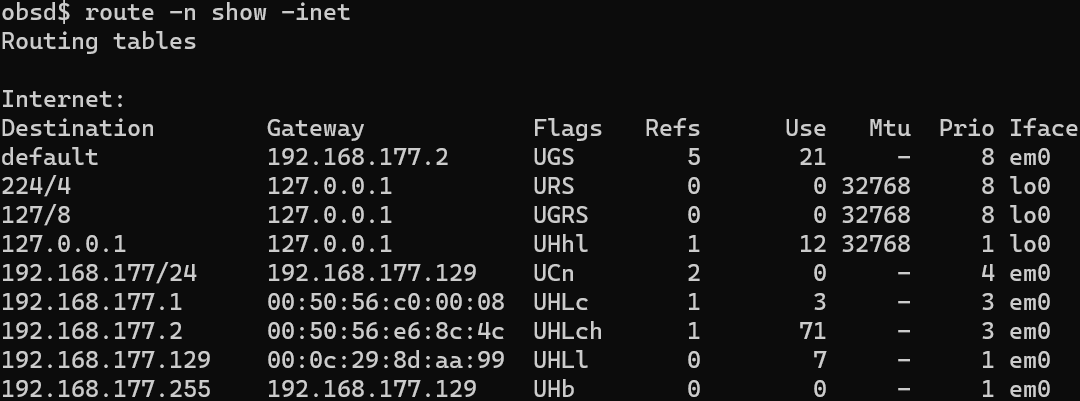
Routing table
What is it?¶
A routing table, also known as routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or network host that lists the routes to distinct network destinations. The routing table contains information about the immediately surrounding network topology.
Routing protocols are responsible for the construction of the routing table. Static routes are entries that are fixed, rather than discovered by routing protocols.
Contents¶
A routing table consists of at least three information fields:
- network identifier: The destination subnet and netmask
- metric: The routing metric of the path through which the packet is to be sent. The route will go in the direction of the gateway with the lowest metric.
- next hop: The next hop, or gateway, is the address of the next station to which the packet is to be sent on the way to its final destination.
Certain applications and implementations can also contain additional values for path selection:
- quality of service associated with the route. For example, the U flag indicates that an IP route is up.
- filtering criteria: ACLs associated with the route
- interface: Such as eth0 for the first Ethernet card.
Example routing table: